Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS) have emerged as a crucial technology in warehouse management, logistics, and manufacturing. By providing real-time asset tracking, inventory visibility, and workflow automation, RTLS optimizes operations, enhances safety, and reduces inefficiencies. The integration of RTLS with Industry 4.0 technologies, including IoT, AI, and automation, is transforming how businesses manage logistics and manufacturing operations.
RTLS enables businesses to track inventory, equipment, and personnel, ensuring a smooth flow of operations. It minimizes search times, improves order fulfillment, and enhances warehouse space utilization. Additionally, RTLS helps reduce errors related to misplaced inventory and stock discrepancies.
Logistics involves complex supply chain operations, and RTLS ensures accurate tracking of goods and vehicles. By providing real-time visibility, RTLS facilitates route optimization, minimizes transportation delays, and improves delivery accuracy. It also supports Just-in-Time (JIT) and Just-in-Sequence (JIS) inventory management, reducing excess stock and preventing understocking.
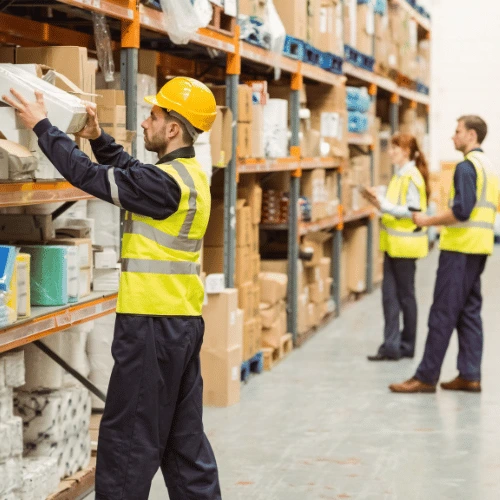
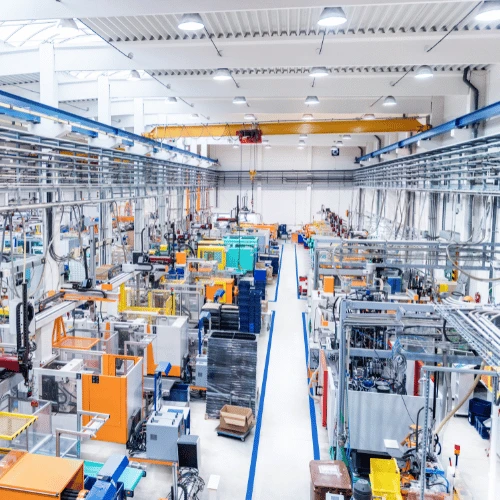


RTLS allows manufacturers to track assets, components, and personnel within production facilities. It reduces downtime, improves machine utilization, and enhances workflow automation. The ability to track materials in real time ensures smooth transitions between pre-assembly and main assembly stages, preventing bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
RTLS enhances safety by monitoring worker movements and hazardous zones. It provides geofencing alerts to prevent unauthorized access, tracks lone workers in high-risk environments, and ensures emergency mustering for rapid evacuation. By analyzing movement patterns, RTLS helps redesign workflows to minimize accident risks.
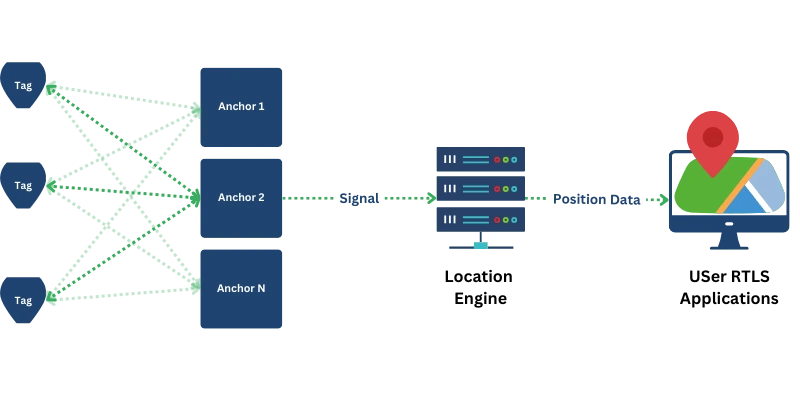
Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS) track assets, personnel, and vehicles within defined areas using tags, anchors, location engines, and user applications. These components enable real-time tracking to optimize logistics and manufacturing. Learn more at RTLS Principles.
Organizational Resistance: Employees requiring training and change management.
Cybersecurity Risks: Wireless systems are vulnerable to hacking and data breaches.
Battery Life: Active tags require frequent recharging or battery replacements.
Environmental Interference: Factors like metal structures and signal interference can affect system accuracy and performance.
Implementation Costs: High initial investment in infrastructure and integration.
Efficient Storage Management: Ensuring optimal warehouse and factory space utilization.
Seamless Integration with ERP/WMS: Providing real-time data for informed decision-making.
Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring worker safety and tracking hazardous materials.
Automated Inventory Updates: Reducing reliance on manual inventory processes.
Accurate Location Tracking: Eliminating misplaced inventory and improving order fulfillment.
Reduces search times for assets and inventory.
Automates workflow processes, minimizing manual interventions.
Enhances route optimization and minimizes transportation delays.
Lowers labor costs by eliminating manual tracking.
Reduces inventory losses due to misplacement or theft.
Optimizes resource utilization and prevents excess stock accumulation.
Enhances real-time personnel tracking for emergency response.
Prevents forklift collisions through proximity alerts.
Secures restricted areas using geofencing technology.
Provides real-time analytics for inventory and asset management.
Improves planning with predictive insights based on historical data.
Enhances compliance by maintaining accurate records of asset movements.
Automated cycle-time tracking for assembly processes.
Ensuring accurate material delivery in Just-in-Time (JIT) manufacturing.
Eliminating production bottlenecks through real-time workflow analysis.
Benefit: Reduced downtime and optimized production schedules.
Use Case: Automating material movement between production lines.
Benefit: Improved inventory visibility and reduced errors.
Use Case: Tracking forklifts to optimize warehouse navigation.
Benefit: Enhanced personnel safety in hazardous locations.
Use Case: Real-time tracking of workers and equipment.
Benefit: Streamlined baggage handling and airport logistics.
Use Case: Tracking aircraft maintenance tools and equipment.
When choosing an RTLS provider, businesses should consider:
Accuracy Requirements: Technologies like UWB and BLE provide sub-meter level accuracy, while RFID and WIFI offer lower precision.
Scalability: Ability to track thousands of assets simultaneously.
Integration Capabilities: Compatibility with ERP, WMS, and IoT platforms.
Power Efficiency: Battery life considerations for active tracking solutions.
Environmental Suitability: Ability to operate in warehouses, outdoor logistics yards, and manufacturing plants.
To learn more about RTLS technologies, visit Comparative Analysis of RTLS Technologies: BLE, UWB, RFID, Wi-Fi, and Hybrid.
Real-time inventory tracking and stock level monitoring.
Optimized storage allocation and space utilization.
Automated workflows for inbound and outbound logistics.
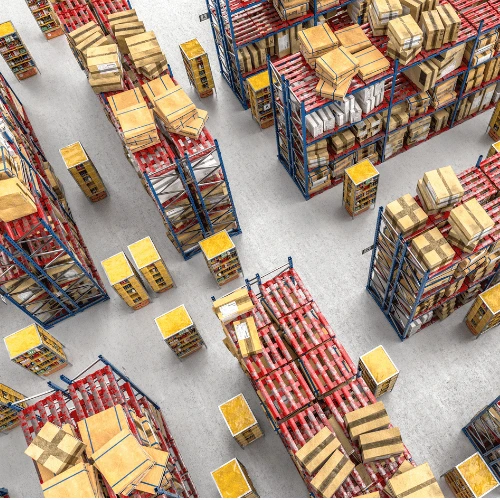

Collision prevention and safety compliance.
Efficient route planning and task automation.
Monitoring vehicle usage and maintenance schedules.
Real-time monitoring of workers in hazardous environments.
Automated emergency mustering for evacuation drills.
Compliance with safety regulations and reporting requirements.
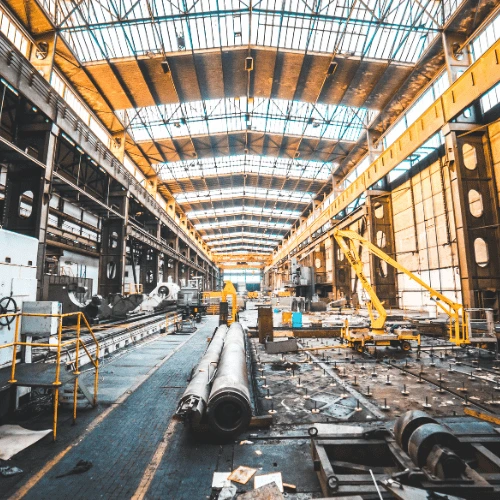

Automated cycle-time tracking for assembly processes.
Ensuring accurate material delivery in Just-in-Time (JIT) manufacturing.
Eliminating production bottlenecks through real-time workflow analysis.
While RTLS offers significant benefits, it has some limitations:
📍 We’re expanding our horizons! Stay tuned for upcoming product and service launches.📍
©2024 anyRTLS, All rights reserved.