Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS) represent a technological framework that enables the automatic identification and tracking of objects, people, or assets in real time. Unlike traditional tracking systems that offer periodic or point-in-time updates, RTLS provides continuous, real-time information about the position and movement of tagged entities within a defined environment. This capability enhances operational efficiency, improves safety, and leads to significant cost reductions.
By delivering precise and actionable location information, RTLS empowers organizations across diverse industries—such as healthcare, manufacturing, logistics, and retail—to achieve better visibility, make informed decisions, and streamline complex workflows.
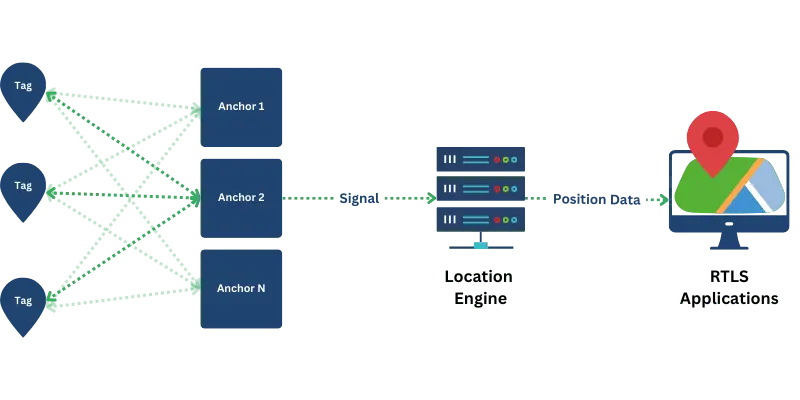
RTLS operate through a sophisticated interplay of signals between tags and receivers, employing multiple technological approaches to achieve precise positioning. At its core, the system utilizes a network of fixed reference points, known as anchors, which are strategically placed throughout the monitored environment. These anchors communicate with mobile tags attached to tracked objects or individuals using various wireless technologies, including Ultra-Wideband (UWB), Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi.
The positioning process involves continuous signal exchange and measurement. When a tag transmits a signal, multiple anchors receive it and analyze various parameters, including signal strength (RSSI), time of arrival (TOA), time difference of arrival (TDOA), and angle of arrival (AOA). Advanced algorithms then process these measurements to calculate the tag’s precise location using techniques such as trilateration or triangulation.
The system updates this information multiple times per second, generating a real-time stream of location data. To improve accuracy and reliability, RTLS often utilize filtering algorithms that consider signal interference, multipath effects, and environmental factors. This processed data is then transmitted to the central system, which maintains a dynamic map of all tracked assets. Building upon this foundational location data, the system can then generate various visualization and analysis tools. Depending on the solution provider, these can include interactive maps for real-time tracking, heat maps showing movement patterns, customizable dashboards displaying key metrics, and detailed reports for historical analysis. These features enable immediate location awareness and support automated decision-making based on predefined rules or triggers.
RTLS is a localized positioning system, distinct from global positioning systems such as GPS. While both GPS and RTLS share foundational elements—time and location—RTLS introduces a crucial third dimension: identification. This integration allows RTLS to offer a comprehensive framework that addresses three essential questions:
1- What is being tracked (Identification)
2- Where the tracked object or person is located (Position)
3- When the tracking information was recorded (Timing)
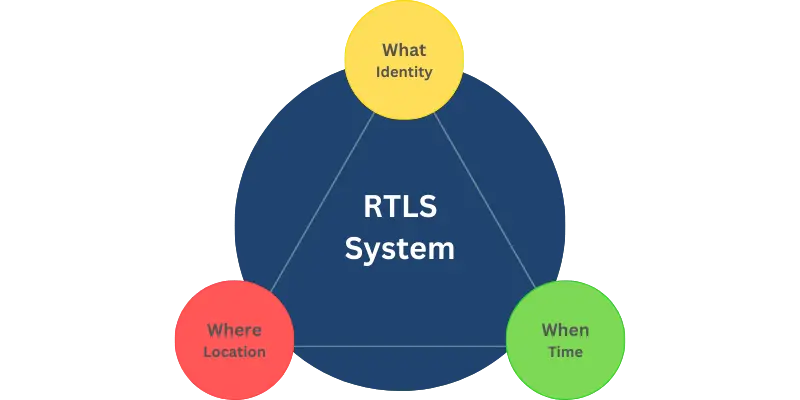
For instance, consider a warehouse scenario in which RTLS are employed to monitor the movement of forklifts. RTLS systems can identify the specific forklift (identification) moving through a particular picking lane (location) at precisely 2:15 PM (timing). This level of detail enhances operational control and supports data-driven decision-making, ensuring that resources are utilized effectively and processes remain efficient.
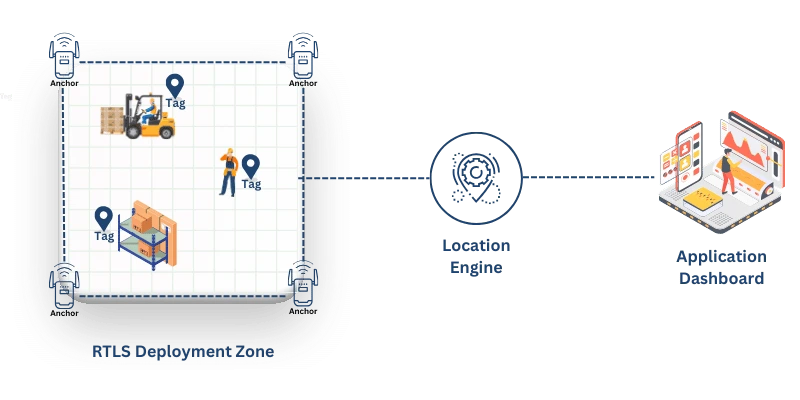
RTLS operates through a combination of hardware components, communication protocols, and software algorithms. All RTLS applications consist of three primary components: transponders (tags), receivers, and software.
Transponders, also known as tags, attach to an item or person to uniquely identify them. These tags emit signals using various technologies such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), Ultra-Wideband (UWB), RFID or Zigbee.
Depending on the application, tags can be passive, semi-passive, or active, each offering varying levels of range and functionality. Passive tags rely on external power sources for activation, while active tags are battery-powered, enabling real-time and extended-range operations. Semi-passive tags combine the characteristics of both.
Receivers, or anchors, are strategically fixed in position within the monitored environment to capture signals emitted by the tags. Depending on the RTLS technology, receivers can include access points, dedicated readers, or even smart devices with appropriate applications. These receivers, collect the transmitted data and relay it to the centralized software for processing.
The software component of RTLS processes the data to calculate the precise location of the tags. It typically comprises firmware embedded in hardware components, middleware connecting hardware to applications, and application software that provides user interfaces for visualization and analysis. Many RTLS software solutions feature dashboards, alert systems, and integration capabilities with enterprise resource planning (ERP) or manufacturing execution systems (MES).
The Application Dashboard in an RTLS system serves as the user interface for monitoring and managing real-time location data. It provides visualizations, alerts, reports, and analytics to help users track assets, personnel, or vehicles efficiently. The dashboard integrates with enterprise systems like ERP and MES, allowing for seamless data flow and decision-making. Customizable alerts and access controls enhance operational visibility and security, making the system more effective for various industries.
RTLS operates using precise methodologies to determine the location of tracked entities within a designated environment. RTLS employs a variety of approaches tailored to meet specific operational needs and environmental challenges. These methodologies utilize advanced signal processing and triangulation techniques to achieve the high level of accuracy and reliability required for real-time tracking.
Each methodology is designed to address unique scenarios, from pinpointing an asset’s exact position within a warehouse to tracking the movement of personnel in complex environments like hospitals or manufacturing facilities. By leveraging these versatile methods, RTLS ensures adaptability across diverse industries and operational contexts.
Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS) deliver significant operational improvements and tangible benefits across industries by providing precise, real-time location data that enhances visibility, decision-making, and efficiency. These systems drive operational excellence through various critical applications that directly impact business performance and safety outcomes.
RTLS transforms asset and inventory management by providing real-time visibility of equipment, autonomous vehicles, and stock. Through strategic deployment of tags and sensors, organizations significantly reduce search times and optimize resource utilization. This capability enables:


Safety improvements represent a crucial advantage of RTLS implementation, as these systems actively monitor personnel and equipment locations to prevent accidents and ensure regulatory compliance:
RTLS drives operational excellence by enabling process automation and providing real-time insights that streamline workflows:


The comprehensive location data generated by RTLS enables organizations to make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency:
RTLS technology improves customer service delivery through personalized, location-aware interactions:

RTLS finds applications across diverse industries, with each deployment tailored to specific operational needs:
RTLS is extensively used to locate medical equipment, monitor patient movements, and enhance staff efficiency. For example, during emergencies, RTLS can quickly identify the nearest available defibrillator, potentially saving lives.
In factories, RTLS improves asset utilization, tracks the movement of raw materials, and optimizes production workflows. Real-time tracking of forklifts and tools ensures efficient operations and reduced downtime.
RTLS streamlines inventory management, reduces errors in order fulfilment, and ensures timely shipment tracking. For instance, a warehouse can use RFID-based RTLS to track pallets as they move through the facility, improving inventory accuracy.
Retailers leverage RTLS to enhance customer experiences by tracking product availability and optimizing store layouts. BLE-enabled systems allow customers to navigate stores more efficiently while enabling personalized marketing through proximity-based notifications.
In construction sites, RTLS ensures worker safety by tracking their locations in real time. Geofencing can alert supervisors if a worker enters a hazardous zone, minimizing the risk of accidents.
Airports use RTLS to manage ground support equipment, track baggage movement, and streamline passenger boarding processes. This reduces delays and enhances operational efficiency.
The effectiveness of Real-Time Location Systems is determined by several fundamental characteristics that influence their performance and applicability across different use cases. Understanding these characteristics is crucial for selecting and implementing the right RTLS solution for specific operational requirements.
RTLS solutions are rapidly advancing, driven by several key technological trends and emerging applications.
The convergence of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) with RTLS is enhancing operational efficiency across various sectors. In manufacturing, AI-powered RTLS enables intelligent automation and data-driven decision-making, optimizing workflows and reducing errors.
In healthcare, AI integration improves patient care by optimizing resource allocation and care coordination.
The advent of 5G technology is set to revolutionize RTLS by providing faster, more reliable networks with reduced latency. This enhancement facilitates real-time data processing, crucial for applications requiring immediate response times, such as autonomous vehicles and augmented reality. In logistics, 5G improves data visibility, allowing for real-time insights into inventory levels and operational statuses.
Energy efficiency remains a critical focus in RTLS development. Innovations such as low-power tags and optimized algorithms are extending battery life and reducing operational costs, which is essential for large-scale deployments. These advancements ensure that RTLS solutions are both sustainable and cost-effective, meeting the growing demand for scalable and efficient location tracking systems.
RTLS is increasingly being utilized to tackle contemporary challenges across various industries. In healthcare, AI-powered RTLS is transforming service delivery by enhancing patient care and operational efficiency. In manufacturing, the integration of RTLS with IoT and AI supports intelligent automation and data-driven decision-making, aligning with Industry 4.0 objectives.
Additionally, in logistics, 5G-enabled RTLS solutions are revolutionizing operations by providing real-time insights into inventory levels and operational statuses, thereby enhancing efficiency and responsiveness.
These emerging trends and technological advancements are propelling RTLS into new realms of application, offering innovative solutions to complex challenges in an increasingly interconnected world.
📍 We’re expanding our horizons! Stay tuned for upcoming product and service launches.📍
©2024 anyRTLS, All rights reserved.