Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) serves as the key enabler of advanced asset tracking by offering wireless identification and monitoring of assets. When integrated with Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS), RFID technology enables precise, continuous tracking of assets, driving efficiency while minimizing manual intervention and empowering data-driven decision-making across industries.
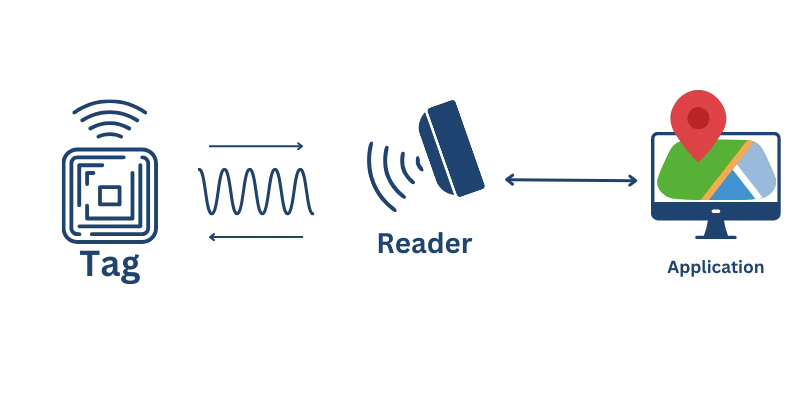
RFID tag systems operate through an interconnected network of components that work together to provide accurate asset tracking capabilities. At its core, the system relies on wireless communication between RFID tags attached to assets and readers that capture and process this information. This communication occurs via radio waves, enabling contactless identification and tracking of assets throughout their lifecycle.
An RFID system comprises three critical components:
Radio waves form the backbone of RFID communication, grouped into three frequency bands based on range and application:
Integrating RFID with RTLS adds another dimension to asset visibility by enabling continuous, real-time location tracking. RTLS enhances RFID’s capability by determining the exact position of items, enabling businesses to monitor workflows, optimize spatial utilization, and reduce manual intervention.
For example, in a warehouse, RTLS tracks assets from storage to shipping zones, eliminating searches and improving productivity. Similarly, in healthcare, RTLS helps locate critical equipment like ventilators or infusion pumps, ensuring availability during emergencies. By automating these processes, RFID-based RTLS systems deliver operational visibility and support data-driven decision-making.
RFID is widely used across industries, with the following examples highlighting its broad applications.
Retailers use RFID to manage inventory more effectively, reduce theft, and enhance customer experiences. By leveraging RAIN RFID protocols, businesses conduct fast inventory checks, track shipping conditions, and maintain live updates on stock levels.
RFID is transforming healthcare environments through enhanced patient tracking and critical asset management. The technology enables healthcare providers to monitor patient locations in real-time, leading to improved care quality and safety protocols. Additionally, it provides efficient tracking of critical medical equipment, from ventilators to surgical tools, ensuring immediate availability when needed and optimizing resource utilization across healthcare facilities.
In factories, RFID systems offer streamlined tool tracking, predictive maintenance for machinery, and monitoring of vehicle fleets over large areas. Unlike barcodes, RFID technology can sustain harsh conditions, such as exposure to dust, water, or extreme temperatures.
Inventory Management
Theft Prevention
Stock Tracking
Patient Tracking
Equipment Management
Safety Monitoring
Asset Tracking
Asset Maintenance
Safety and Security
RFID-based tracking systems deliver clear operational benefits and financial returns.
RFID eliminates ambiguity in asset management. Minimizing manual errors, allows businesses to precisely track inventory, equipment, or personnel in real time. Paired with RTLS technology, RFID systems ensure that every movement within a facility is accounted for, providing operational transparency.
RFID automates traditionally labor-intensive processes like inventory audits, reducing costs associated with manual tracking. For example:
RFID systems provide measurable ROI (Return on Investment) by significantly lowering inefficiencies, minimizing asset misplacement, and reducing waste. While the initial investment in tags, readers, and software may seem substantial, these costs are quickly offset by long-term operational savings, productivity boosts, and reduced labour expenses.
RFID tags serve as asset identifiers and are classified into three main types based on their power source and communication capabilities:
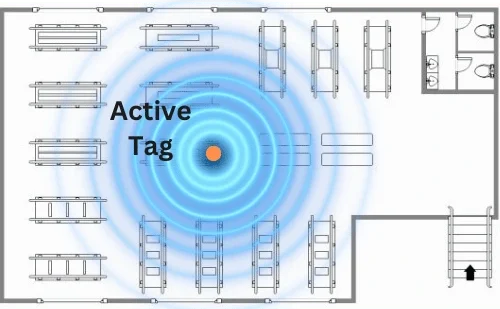
Active RFID tags contain their power source, typically a battery, which enables them to transmit signals independently over long distances. These tags can achieve read ranges of several hundred meters and often include additional capabilities such as environmental sensing. Their independent power source makes them ideal for real-time tracking applications where continuous monitoring is essential.
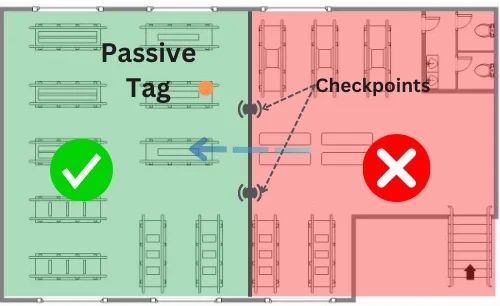
Passive RFID tags operate without an internal power source, instead drawing power from the electromagnetic field generated by the reader. While their read range is shorter, typically just a few meters, they offer distinct advantages in terms of cost and durability. Their simplified design means they can operate indefinitely without battery replacement, making them perfect for high-volume applications where cost-effectiveness is crucial.
Semi-passive tags represent a middle ground, using a battery to power their internal circuitry while still relying on the reader’s signal for communication. This hybrid approach offers enhanced processing capabilities and improved reliability compared to passive tags while maintaining a more moderate cost than active tags. They excel in applications requiring longer read ranges or operation in challenging environments.
RFID data retrieval is performed by readers, which varies based on their form factor and usage:
Fixed RFID Readers: Installed at strategic points like entry gates or conveyor belts, fixed readers are ideal for environments requiring continuous tracking, such as warehouses and factories.
Handheld RFID Readers: These portable devices provide flexibility in scanning assets, particularly in retail or stocktaking scenarios where mobility is essential.
Wearable RFID Scanners: Designed for ergonomic use, wearable scanners improve efficiency in high-paced environments where hands-free operation is required, such as assembly lines.
RFID systems employ robust encoding techniques to enhance performance:
Protocols have a key role in enabling seamless integration across devices and systems:
These techniques and protocols ensure reliable, efficient data transfer, enabling RFID systems to integrate seamlessly with enterprise operations.
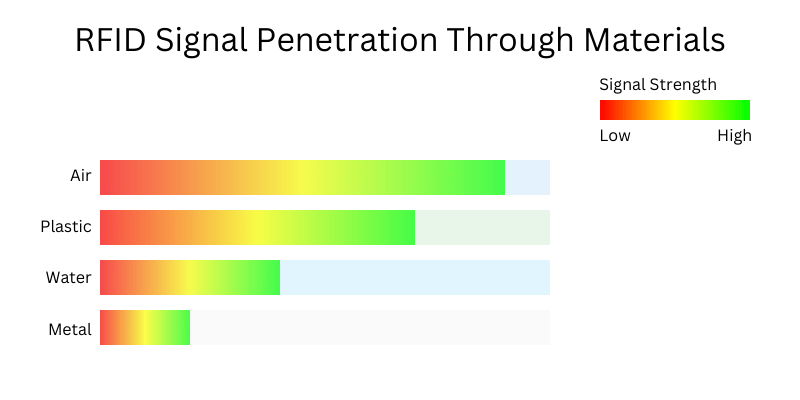
The effectiveness of RFID systems is influenced by several factors:
RFID paired with RTLS technology is revolutionizing asset tracking by combining real-time location data with seamless identification capabilities. As industries increasingly demand data-driven decisions, RFID systems deliver unmatched visibility, efficiency, and scalability. With applications ranging from healthcare to supply chains, RFID offers a robust and future-ready solution for modern enterprise challenges.
RFID is a key solution to transform how businesses manage their assets, cut costs, and enhance operational performance.
📍 We’re expanding our horizons! Stay tuned for upcoming product and service launches.📍
©2024 anyRTLS, All rights reserved.